WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing, Wiki), bearing schemes are Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing (CWDM), Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) as well as Medium Wavelength Division Multiplexing (MWDM), and Fine Wavelength Division Multiplexing (LWDM). The following is the introduction of each scheme.
Contact Author: [email protected]. TEL: + 86 137 1427 7453
CWDM (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexer)
CWDM (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexer) is a sparse wavelength division multiplexer, also known as a coarse wavelength division multiplexer. CWDM has 18 different wavelength channels, each with different wavelengths separated by 20 nm, using wavelengths from 1270 nm to 1610 nm.
CWDM supports fewer channels than DWDM because it is compact and cost-effective, making it an ideal solution for short-range communications. the biggest advantage of CWDM systems is their low cost, with device costs mainly in filters and lasers.
The wide wavelength interval of 20nm also gives CWDM the advantage of low technical specifications of the laser and simplified structure of the optical multiplexer/demultiplexer. The structure is simplified, and the yield rate is increased, so the cost is reduced.
DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexer)
DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexer) is a dense wavelength division multiplexer. the channel spacing of DWDM is 1.6/0.8/0.4 nm (200 GHz/100 GHz/50 GHz), which is much smaller than CWDM.
Compared with CWDM, DWDM with tighter wavelength spacing can carry 8 to 160 wavelengths on a single fiber, which is more suitable for long-distance transmission. With the help of EDFA, the DWDM system can work in the range of thousands of kilometers.
FWDM (Filter Wavelength Division Multiplexer)
FWDM (Filter Wavelength Division Multiplexing) filter chip type WDM, is based on the mature thin film filter technology. Filter WDM can combine or separate different wavelengths in a wide wavelength range, and is widely used in erbium-doped optical amplifiers, Raman amplifiers, and WDM fiber networks.
MWDM (medium wavelength division multiplexer)
MWDM is to reuse the first 6 waves of CWDM, compress the 20nm wavelength interval of CWDM to 7nm, and use TEC (Thermal Electronic Cooler) temperature control technology to realize 1 wave expansion to 2 waves. This achieves the capacity increase and further fiber saving.
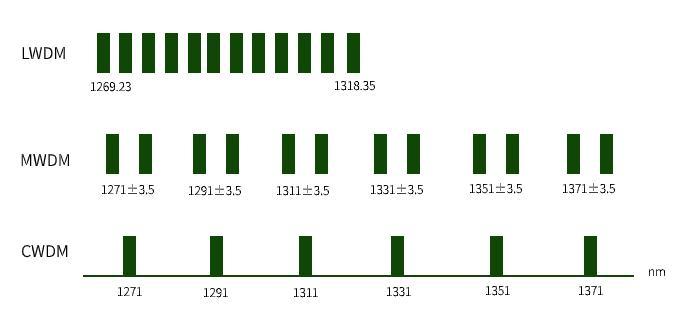
MWDM is based on CWDM 6 waves, left and right offset 3.5nm expansion to 12 waves (1267.5, 1274.5, 1287.5, 1294.5, 1307.5, 1314.5, 1327.5, 1334.5, 1347.5, 1354.5, 1367.5, 1377.5, 1374.5nm).
LWDM (fine wavelength division multiplexing)
LWDM is an Ethernet channel-based wavelength division multiplexing Lan-WDM technology, also known as fine wavelength division multiplexing. Its channel spacing is 200 to 800GHz, and this range is between DWDM (100GHz, 50GHz) and CWDM (about 3THz).
LWDM uses 12 wavelengths in the 1269nm to 1332nm band located in the O-band (1260nm to 1360nm) range with a wavelength interval of 4nm (1269.23, 1273.54, 1277.89, 1282.26, 1286.66, 1291.1, 1295.56, 1300.05, 1304.58, 1309.14, 1313.73, 1318.35 nm).
LWDM operating wavelengths are characterized by being located near zero dispersion, small dispersion, and good stability. Meanwhile, LWDM can support 12-wave 25G with enhanced capacity, which can further save fiber.
Key2Optics has full product lines for passive and active WDM products.